Keeping a balanced and diverse population of gut bacteria is essential to staying healthy. The gut microbiome is made up of trillions of bacteria that live in the human stomach and intestines. These microbes play an important role in digesting food, regulating immune function, producing vitamins and protecting against pathogens.
The human body is home to trillions of microorganisms referred to as “good” or “friendly” bacteria, which help us in a number of ways. Unfortunately, modern life tends to disrupt the natural balance between good and bad bacteria.
As a consequence, most people have an unbalanced microbiome with too few good bacteria and too many bad ones. Reducing stress, cutting back on sugar, eating more prebiotic foods and taking probiotic supplements are proven ways to help bring things back into balance again.
What Are Probiotics?
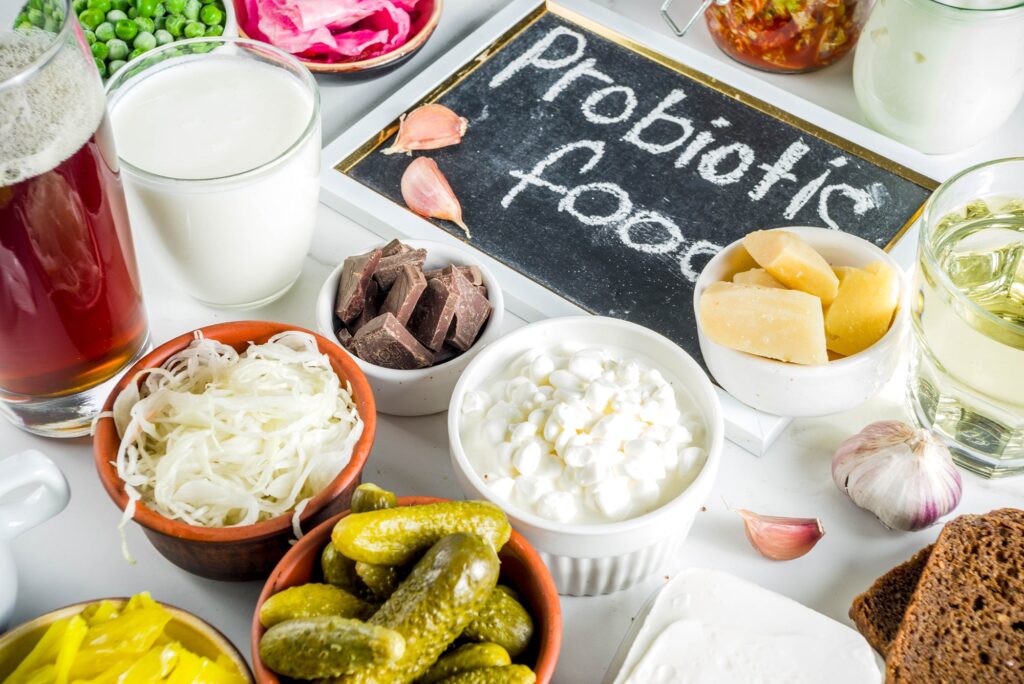

If there were a “good bacteria Hall of Fame”, one of the top probiotics would be Lactobacillus species. It’s a genus of bacteria that’s found in yogurt, kefir and other fermented foods. Lactobacillus is a particularly helpful probiotic that fights off bad bacteria in the gut and helps people tolerate the lactose in milk.
Other top probiotics include Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus and Escherichia coli Nissle (or E. coli Nissle). These bacteria are common in the human gut and have a range of benefits, including boosting immunity and reducing inflammation.
The best way to describe probiotics is as live microorganisms that have health benefits for the host in which they are being grown and/or consumed. The microorganisms are not only helpful to the host, but have no negative effects whatsoever, so they are also referred to as being “friendly” microorganisms.
Most probiotics originate from dairy products, but they can also be found in other foods such as fermented vegetables, fermented soybeans and fermented beverages.
Why Is Maintaining a Healthy Gut So Important?

The number of different bacterial species in the gut microbiome varies greatly from person to person. The average person has between 400 and 1,000 species but some people have as few as 100 species while others have over 1,500!
Unfortunately, there is no “ideal” gut microbiome. Instead, the microbiome needs to be balanced and diverse. An imbalanced microbiome may be linked to a variety of health issues, including irritable bowel syndrome, obesity, diabetes, allergies and skin problems such as acne.
In addition, a weakened immune system, poor digestion and an overload of toxins in the body are all potential consequences of an unhealthy gut. In fact, scientists believe that an unhealthy gut may be an underlying cause of many modern diseases.
What Happens When You Don’t Have Enough Good Bacteria?

When the gut microbiome is out of balance, there are too few “good” bacteria. As a result, harmful “bad” bacteria have more room to thrive. The bad bacteria release toxins that travel to the liver and kidneys, where they are broken down.
As the metabolites travel through the body, they can cause all sorts of symptoms. If you don’t have enough good bacteria, you’re more likely to experience symptoms such as gas, bloating and abdominal cramps. You’re also at a greater risk of developing a bacterial infection such as food poisoning or a more serious infection like sepsis.
How to Maintain a Healthy Gut Environment

If you want to maintain a healthy gut environment, it’s important to maintain a healthy diet — and lifestyle — to ensure that the microbiome is in good shape. Here are a few ways to do that: Reduce stress. Chronic stress weakens the immune system, which makes it easier for bad bacteria to thrive in the gut.
However, there are plenty of ways to reduce stress in your life, including meditation, exercise and mindfulness. Cut back on sugar. A high sugar diet can disrupt the balance between good and bad bacteria in the gut by feeding harmful bacteria. To keep things in check, try to minimize your sugar intake. Eat more prebiotic foods.
They feed the good bacteria already in your gut so that they have the nutrients they need to fight off the bad bacteria. Common prebiotic foods include asparagus, artichoke, asparagus and leeks. Take probiotic supplements. Taking probiotic supplements can help to restore the good bacteria in your gut. They’re often found in yogurt, but they are also available in capsule form.
Avoid Processed Foods

One way to reduce stress in your life is to avoid as many processed foods as possible. This is important because one way to reduce the amount of good bacteria in the gut is by eating too many processed foods. Processed foods are usually high in sugar and low in fiber, which are both detrimental to the health of the microbiome. In short, processed foods often have low nutritional content.
By eating high-quality, unprocessed foods, you can ensure that you’re providing your gut with the nutrients it needs to stay strong and healthy. This includes plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits, seeds, nuts, beans and grains. You can also try to incorporate probiotic-rich fermented food into your diet each day.
Eat More Fiber and Vegetables

Many people don’t get enough fiber in their diets. Eating more fiber, particularly from vegetables, can help to promote a healthy gut microbiome as it feeds beneficial bacteria. Vegetables such as artichokes, asparagus, leeks, broccoli and Brussels sprouts are particularly high in fiber. Eating more vegetables will help to improve digestive health as well.
The more vegetables you eat, the less room there is for other less-nutritious foods such as sugar and processed grains. This keeps the microbiome healthy and provides the body with much-needed fiber, vitamins and minerals.
This can help to reduce the risk of diabetes, heart disease and certain types of cancer. Including immune system support supplements like Quercetin and NAC into your daily routine is an effective way of supplying your body with the vitamins and minerals it needs in order to function optimally and maintain a healthy digestive system.
Exercise Consistently

Exercising regularly is one of the best ways to reduce the amount of stress in your life and to promote a healthy gut microbiome. It’s also a great way to improve your general health and well-being. There are a number of ways to exercise, including running, swimming, cycling and weightlifting.
One of the easiest ways to incorporate exercise into your daily routine is to walk more often. You can walk to the store, walk your dog or walk to work — there are plenty of ways to get more walking into your life. Regular exercise can also help you to lose weight, which can reduce the amount of bad bacteria gut.
Bottom line
The human gut microbiome is one of the most densely populated regions of bacterial life on Earth. It houses about 100 trillion bacteria, making up about 3 pounds of your body weight. The microbiome is responsible for processing your food, regulating your immune system and producing vitamins.
Unfortunately, modern life can disrupt the natural balance between good and bad bacteria. If you want to maintain an optimal level of good bacteria in the gut, it’s important to keep a healthy diet and exercise regularly. You can also take probiotic supplements to help promote a healthy gut environment.